-
A Because aluminum offers better long-term reliability, corrosion resistance, and lower structural impact, especially in demanding environments.
-
A Yes.
-
A Aluminum roofing requires minimal but proactive maintenance to preserve its durability and appearance, focusing on preventive care and early issue detection:Regular Cleaning,Coating Inspection,Drainage Maintenance,Physical Damage Check,Avoid Harsh Chemicals.
-
A Yes.
-
A Yes.
-
A Normally from 0.5-3.0mm thickness.
-
A High-quality coatings such as PVDF offer excellent color retention and UV resistance, minimizing fading over long-term exposure.
-
A Yes.
-
A Aluminum roofing profiles include:
1.Corrugated sheets,
2.Trapezoidal panels,
3.Standing seam panels,
4.Custom roll-formed profiles.
-
A When correctly installed such as prodcued by sandwich panel , together with underlay,cobined with proper insulation,Aluminum roofing noise level will much better than s are other metal roofing systems.
-
A Yes.
-
A PE Coating will be last 8-12 years,
HDP or SMP coating will be last round 15 years.
PVDF coating will be as long as 25 years or even more.
-
A HDP,SMP,PVDF,PE.
-
A Yes.
-
A In real projects, aluminum roofing outperforms steel roofing in key aspects like weight, corrosion resistance, and long-term maintenance, though steel may offer lower initial costs in some cases. Aluminum’s low density (2.7 g/cm³ vs. steel’s 7.85 g/cm³) makes it significantly lighter, reducing structural load and installation complexity—critical for large-span or retrofitted roofs. Its natural corrosion resistance (enhanced by alloys like 5052/5083 with Mg/Cr) eliminates rust risks in harsh environments (coastal, industrial), unlike steel which relies on coatings that degrade over time, requiring frequent repainting or galvanizing. Aluminum also boasts a superior strength-to-weight ratio, enabling thinner profiles for equivalent load-bearing capacity, while steel demands thicker gauges for similar strength. Maintenance-wise, aluminum’s durable pre-painted coatings (e.g., PVDF, 10–20-year lifespan) minimize upkeep, whereas steel roofs often need periodic rust prevention. Though steel may be cheaper upfront, aluminum’s longevity (30+ years vs. steel’s 15–25 with maintenance) and lower lifecycle costs make it preferable for projects prioritizing durability, aesthetics (custom colors/textures), and sustainability (100% recyclability). Steel, however, remains viable for budget-focused applications in mild climates where corrosion risks are low.
-
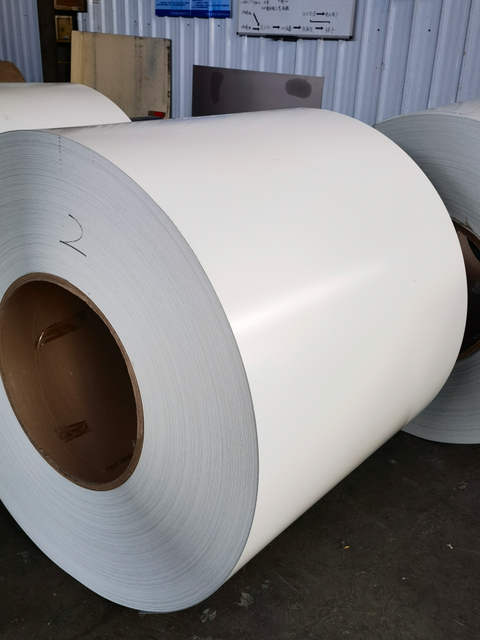
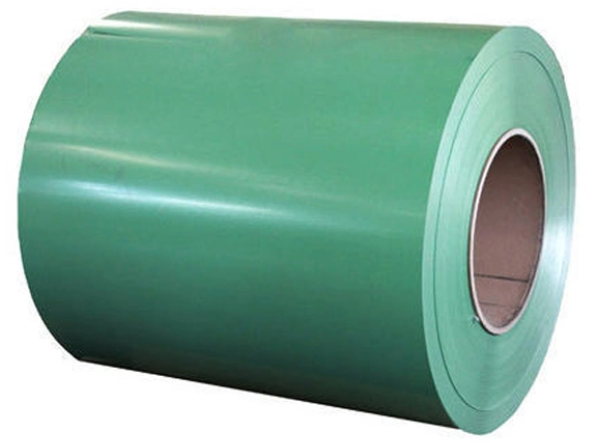
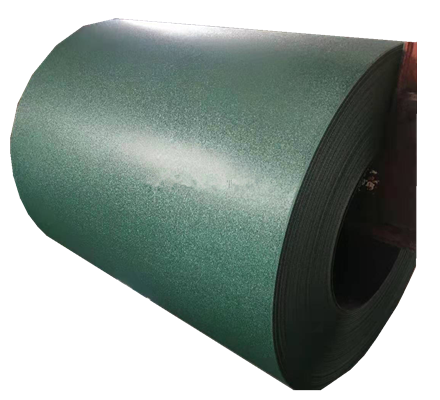
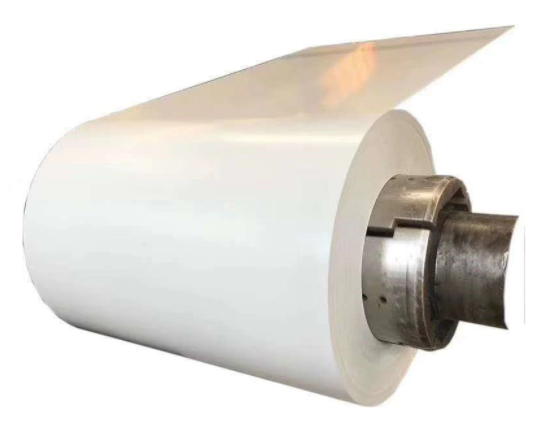
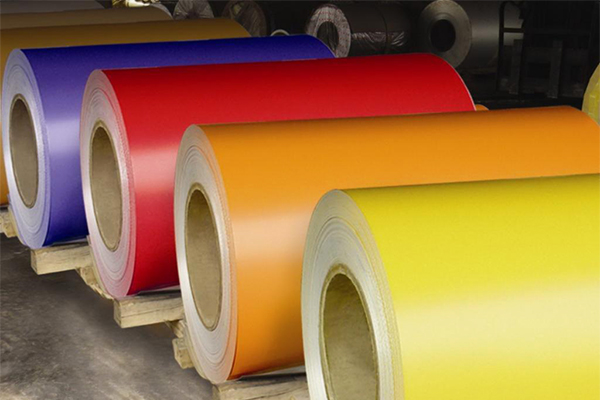
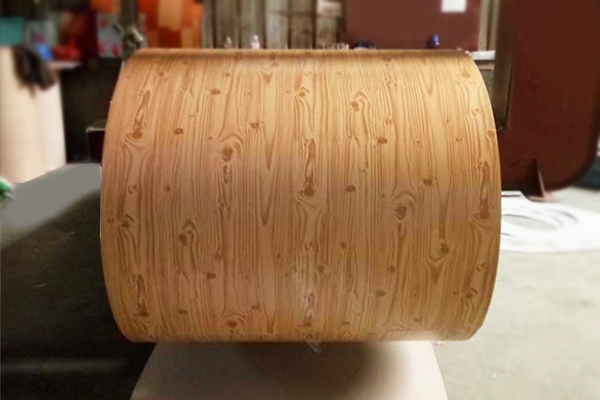
A Color coated aluminum is widely used in modern roofing systems because it uniquely combines aesthetic appeal with exceptional functional performance tailored to outdoor demands. Its pre-coated surface, featuring printed or digitally applied patterns (such as wood grain, stone, or solid colors), elevates architectural design while the aluminum substrate provides inherent advantages: lightweight construction reduces structural load, high strength resists deformation, and natural corrosion resistance ensures longevity. The protective coating further enhances durability by shielding against UV radiation, rain, and temperature fluctuations, preventing fading, chalking, or peeling—minimizing maintenance needs over decades. Additionally, its ease of fabrication into complex roof shapes, combined with optional thermal insulation or reflective properties (in some variants) that aid energy efficiency, aligns with modern priorities for sustainable, low-maintenance building solutions. This blend of visual flexibility, robust performance, and cost-effectiveness makes it an ideal choice for contemporary roofs seeking both style and reliability.
English
العربية
Français
Русский
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
हिन्दी
فارسی
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Latine
Dansk
Shqip
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
latviešu
Azərbaycan dili
Беларуская мова
ქართული
íslenska
Kinyarwanda
Lietuvių
Lëtzebuergesch
Македонски
Malti
Türkmençe
ئۇيغۇرچە
Cymraeg


 GENERAL PARAMETERS
GENERAL PARAMETERS